Our article Photon-Counting Computed Tomography-Based Hepatic iron Quantification Using a Tungsten-Based Contrast Agent has been published in Investigative Radiology.
https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000001189
Abstract:
Objectives
This study explores the potential of quantifying hepatic iron in computed tomography (CT) scans in the presence of iodine (I)- or tungsten (W)-based contrast media (CM).
Materials and Methods
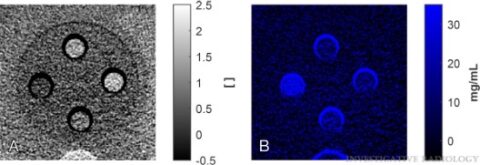
Experimental work was performed on a commercial photon-counting CT system able to simultaneously acquire up to 4 spectral data sets in a single scan. We examined 2 anthropomorphic abdominal phantoms with material samples of liquid liver tissue surrogate, fat, iron, and I- or W-based CM to mimic different liver compositions in an enhanced CT scan. Iron was quantified by material decomposition of reconstructed spectral CT images.
Results
Two-material decomposition based on 2 spectral data sets provided material images of iron and liver with an accuracy of 1.4 mg/mL in the iron image of CM-free samples. The presence of W affected the iron quantification: For 2 and 4 mgW/mL in the material samples, the iron concentration was overestimated (P < 0.05) with accuracies of 2.7 and 4.7 mg/mL, respectively. Three-material decomposition based on 4 spectral data sets provided material images of iron, liver, and W, with an accuracy of 1.4 mg/mL in the images without W and 1.5 (nonsignificant difference, P > 0.07) and 1.6 mg/mL (overestimation, P > 0.03) in the iron image at 2 and 4 mgW/mL, respectively. The presence of I affected the iron quantification more than W in both 2- and 3-material decomposition: For 2 and 4 mgI/mL in the material samples, the measured iron concentration was even higher (P < 0.05), with accuracies >18 and >37 mg/mL, respectively.
Conclusions
The accuracy of iron quantification from a 3-material decomposition suggested clinically feasible detection and quantification of critical hepatic iron levels in enhanced CT scans with suitable CM. In a 2-material decomposition, severe pathology is required to detect an iron liver. W-based CM was superior to I-based CM.